Stand up for the facts!
Our only agenda is to publish the truth so you can be an informed participant in democracy.
We need your help.
I would like to contribute
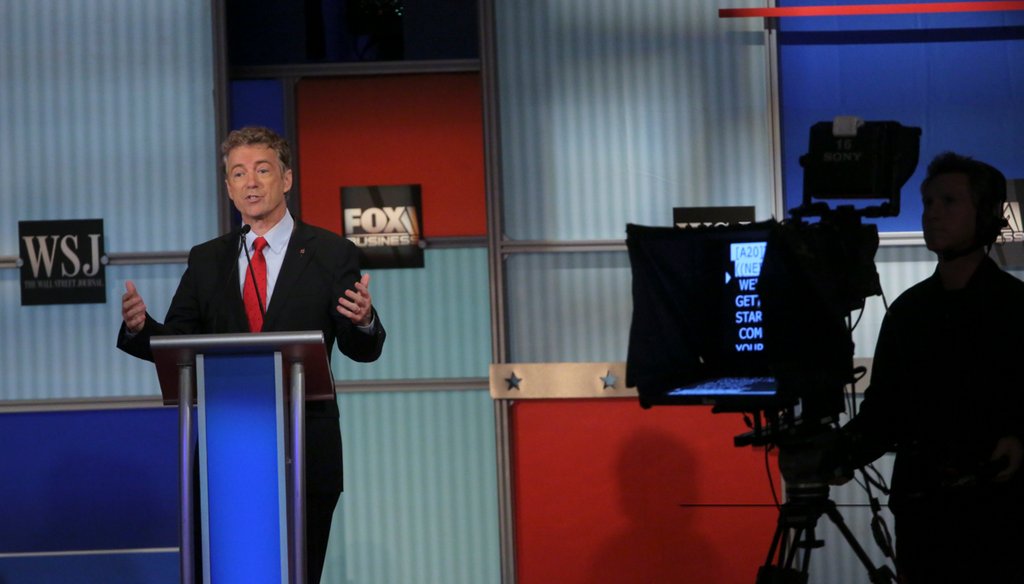

Sen. Rand Paul, R-Ky., speaks during the Republican debate, at the Milwaukee Theatre in Milwaukee, Nov. 10, 2015. (Michael Appleton/The New York Times)
At debate, Rand Paul says income inequality is worse in cities run by Democrats
Where do you find income inequality? In cities run by Democrats, said Sen. Rand Paul, R-Ky.
"I think we ought to look where income inequality seems to be the worst," Paul said during the fourth Republican presidential debate, hosted by Fox Business Network Nov. 10. "It seems to be worst in cities run by Democrats."
We fact-checked a similar claim Paul made last year and found it to be Half True. Let’s revisit what we uncovered.
We used a 2014 study by the Brookings Institution that ranked the top 10 and bottom 10 cities by income inequality. Brookings updated the report in March 2015, and there were a couple changes to the rankings (based on 2013 data). We’ll go with the updated list.
There appears to be something to what Paul said.
Of the study’s 10 most unequal cities, nine have Democratic mayors. They are Atlanta, San Francisco, Boston, Washington, New York, Dallas, Chicago, Los Angeles, and Minneapolis. Only one, Miami, has a Republican mayor.
By contrast, five of the 10 most equal cities have Republican mayors -- Albuquerque; Oklahoma City; Mesa, Ariz.; Colorado Springs, Colo.; and Virginia Beach, Va. The other five either have a nonpartisan mayor (Raleigh, N.C.; Las Vegas; and Arlington, Texas) or a Democrat (Columbus and Nashville).
So on the numbers, Paul has a point. The question is, does this factoid mean anything? Experts we spoke to urged taking the claim with a grain of salt -- if not a whole shaker. Here are a few reasons why.
Mayors aren’t all-powerful players in the local economy.
Where claims of this sort are made, PolitiFact tries to establish whether credit or blame is deserved. In this case, then, is it reasonable to attribute patterns of inequality exclusively, or even primarily, to a mayor?
No -- many factors play into a city’s economic success. The mayor of Detroit doesn’t have much power over the international market for automobiles, and no mayor of New York can take all the credit for the economic juggernaut of Wall Street. While mayoral policies may have an effect on the margins, such factors as the state and national business cycle, broad demographic patterns and international business trends tend to have a much greater impact on economic inequality in cities.
In addition, it’s worth remembering that "cities attract people on the basis of many factors, of which the party of their political leaders is probably a minor one," said William Frey, a senior fellow in Brookings’ Metropolitan Policy Program.
Inequality patterns in cities may be at least as much about population size and geographic patterns as they are about partisan leadership.
Focusing on the partisan differences obscures a more fundamental difference between the most and least unequal cities. The more unequal cities tend to be very big, and the less unequal cities tend to be more modestly sized.
The median population of the 10 most unequal cities on the Brookings list is more than 700,000, compared to about 430,000 for the most equal cities. (If you use the mean instead, the average population of the 10 most unequal cities would be even higher -- 1.9 million versus 500,000.) So it’s not exactly apples-to-apples if you compare the attributes of New York, Los Angeles and Chicago on the one hand with those of Colorado Springs, Virginia Beach and Arlington on the other.
Featured Fact-check
All other things being equal, larger cities tend to have a wider distribution of incomes on both extremes, since they have more residents. That, almost by definition, means larger ratios between the top and the bottom. In the meantime, big cities tend to attract more wealthy people -- i.e., people who can choose to live anywhere they want -- because megacities are likelier to have world-class amenities.
"The real wealth ‘peaks’ tend to be in the big cities, so they have high tops as well as lower bottoms, while the income profiles of smaller localities are typically more ‘compressed,’ " said Jamie Peck, a professor of geography at the University of British Columbia who has studied urban and political patterns in the United States.
How old a city is can matter, too, said Jed Kolko, the chief economist and vice president of analytics at the real estate website Trulia. In older cities many middle-income residents have relocated to the suburbs, leaving behind higher levels of inequality. By contrast, newer cities -- such as Mesa (which is near Phoenix) or Arlington (which is near Dallas) -- often contain many suburban areas or are, in effect, suburbs themselves, Kolko said. Such cities tend to have more modest income ranges.
Why does all this matter? It undercuts the notion that partisan leadership has much to do with why certain cities become relatively unequal and certain become relatively equal.
Causation may actually run the opposite way.
It’s always important to remember that correlation does not necessarily mean causation. In this context, it’s not necessarily that Republican leadership creates greater equality, as Paul’s comment presumes. Rather, it could be that greater equality prompts people to vote Republican. Or it could be unrelated.
"I think it runs more in the direction that inequality provides conditions for Democratic success, rather than Democrats causing inequality," said Michael McDonald, a University of Florida political scientist who specializes in electoral patterns and geography. And any explanation other than political leadership causing greater equality weakens Paul’s point.
The pattern holds only if you look at cities, not metropolitan areas.
If you look at Kolko’s research -- which studied inequality in broader metropolitan areas, rather than in cities per se -- Paul’s pattern falls apart.
As of 2014, of the 10 metropolitan areas with the most equality, only one has a Republican mayor -- Colorado Springs. The other nine either have a Democratic mayor, a nonpartisan one, or no mayor at all because they’re an unincorporated area. This list includes Lakeland-Winter Haven, Fla.; Allentown, Pa.; Salt Lake City; Bethesda-Rockville-Frederick, Md., Tacoma, Wash.; Las Vegas; Cape Coral-Fort Myers, Fla.; Raleigh; and Palm Bay-Melbourne-Titusville, Fla.
What Paul’s office says
Brian Darling, a former spokesman for Paul, told PolitiFact last year that the senator was not simply casting aspersions on Democratic mayors’ handling of their cities’ economies. "What he was saying is that Democrats are not solving the problem," Darling said. "It may be an unsolvable problem. Democrats love to talk about the issue and have been allowed to position themselves as the warriors for those harmed by income inequality, yet they are not a party of action" on this issue.
That’s a reasonable point, but we think a typical listener hearing Paul’s comment would have assumed that he was arguing that Republican policies have promoted greater equality in cities than Democratic policies have. And as we’ve found, that’s far from clearcut.
Our ruling
Paul said that income inequality "seems to be worst in cities run by Democrats."
He has a point that one credible study shows a fairly strong correlation between low inequality and a Republican mayor. But experts say it’s a stretch to draw conclusions from this. The claim inflates the actual powers of mayors to shape inequality in their cities and it ignores the role of population size and suburbanization in driving inequality. It also glosses over the fact that metropolitan areas, as opposed to cities, show no such relationship.
The claim is partially accurate but leaves out important details, so we rate it Half True.
Our Sources
PolitiFact, "Rand Paul says income inequality is worse in cities with Democratic mayors," Sept. 16, 2014
Brookings, "Some cities are still more unequal than others —an update," March 17, 2015
Browse the Truth-O-Meter
More by Lauren Carroll
At debate, Rand Paul says income inequality is worse in cities run by Democrats
Support independent fact-checking.
Become a member!
In a world of wild talk and fake news, help us stand up for the facts.